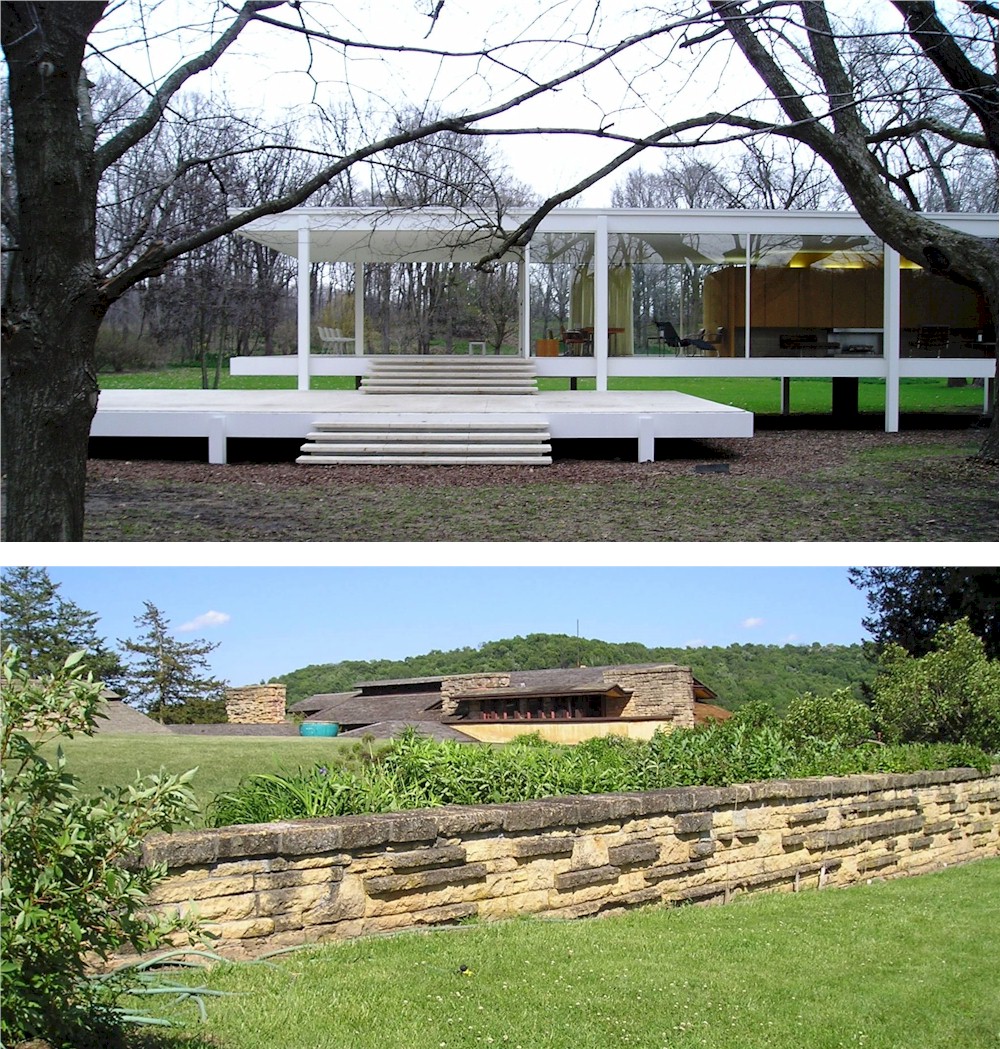
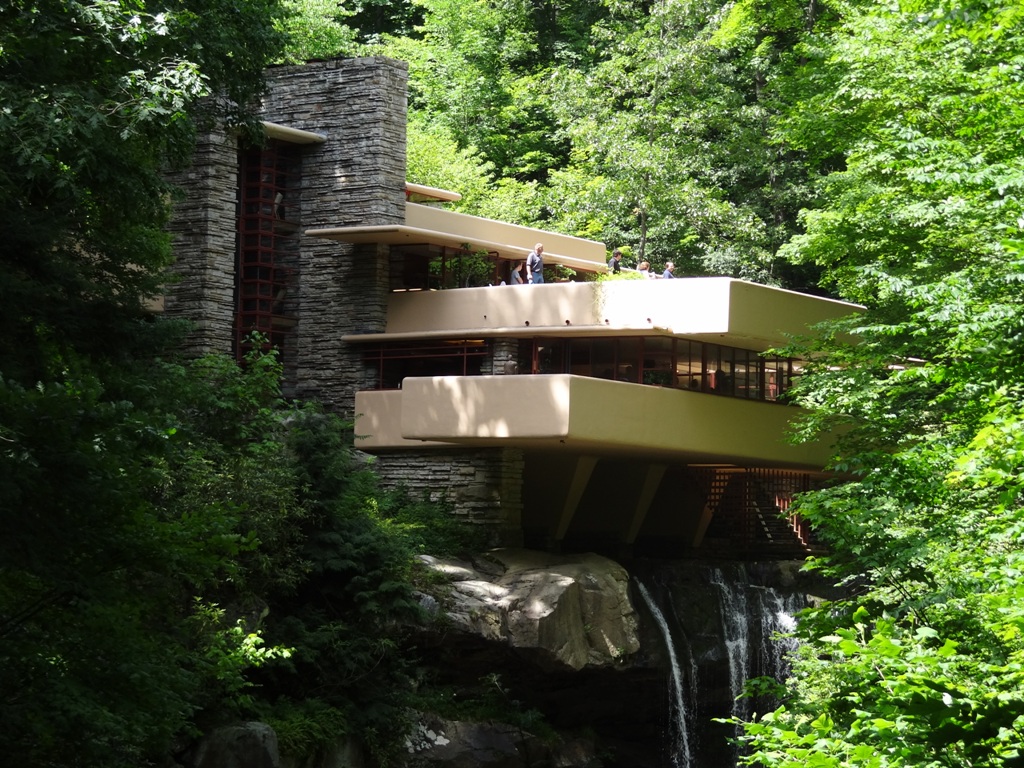
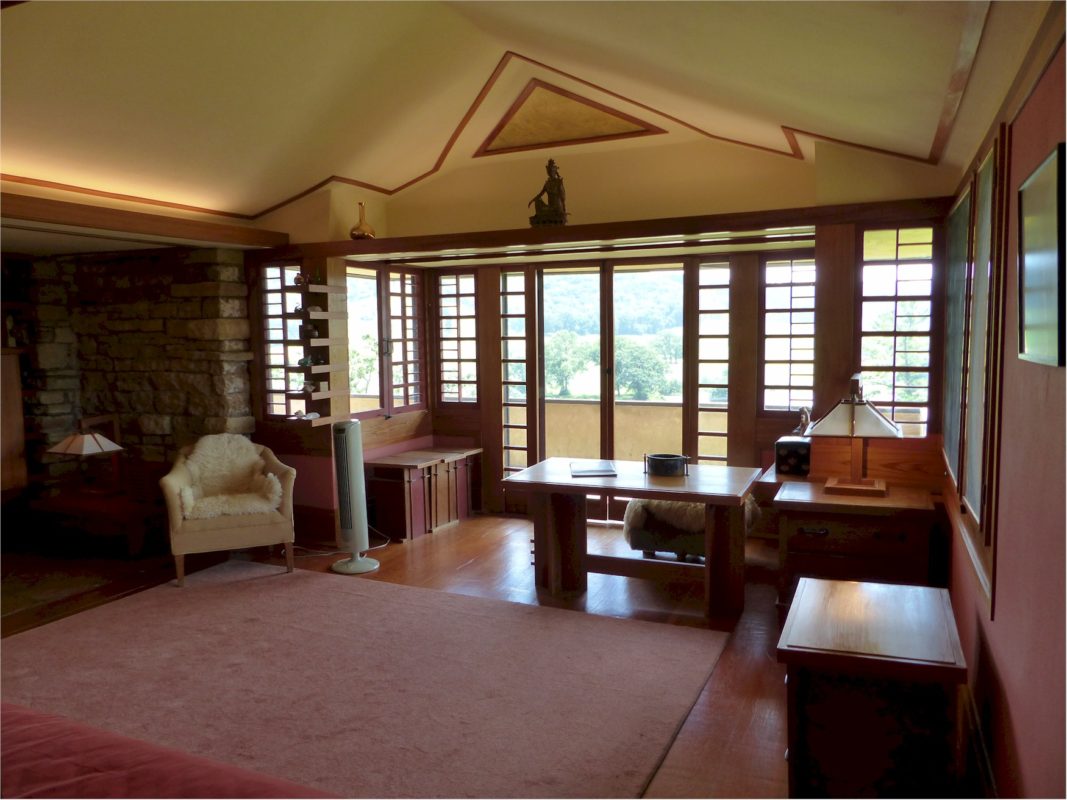
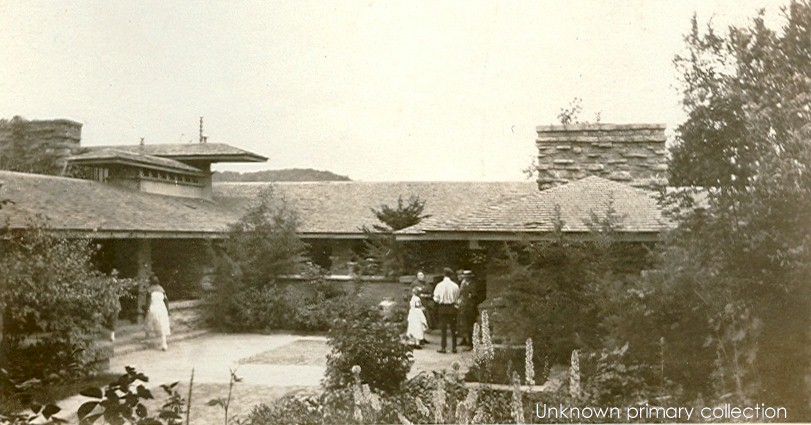
Two pictures of the Midwest in Spring: the top shows the Farnsworth House, by Mies van der Rohe, in Plano, IL in early April. The bottom shows Taliesin, and was taken in early June. Taliesin, in Wisconsin, is 3 hours north of the Farnsworth House.
I looked into architect Ludwig Mies van der Rohe (1886-1969) and Taliesin/Wright after May 12. That was the day I saw the talk about Mies’ Farnsworth House: “Past, Present, and Future of Farnsworth House” on-line through the Vernon Area Public Library (Illinois).
Mies van der Rohe in the U.S.:
German-born “Mies” came to the United States in 1937. The next year he became the head of architecture at the Armour Institute in Chicago, which later became the Illinois Institute of Technology. He was at IIT until 1958, and remained in Chicago for the rest of his life (he became a United States citizen in 1944).
Mies visited Taliesin around the time that he started to teach at IIT in 1938. Mies was visiting with two young architects (Bertrand Goldberg and Bill Priestley) in his new home of Chicago, when the two men decided to call Frank Lloyd Wright on the telephone and see if they could bring Mies to visit Taliesin (three and a half hours away).
That must have been exciting for all of them. Even at that time, Mies and Wright were major figures in world architecture. I hope it was worth their while because, while not planning to, Mies and Goldberg spent four days at Taliesin (Priestley left after one day). All the while, Goldberg acted as a translator, since Mies did not yet speak English.
Mies at Taliesin:
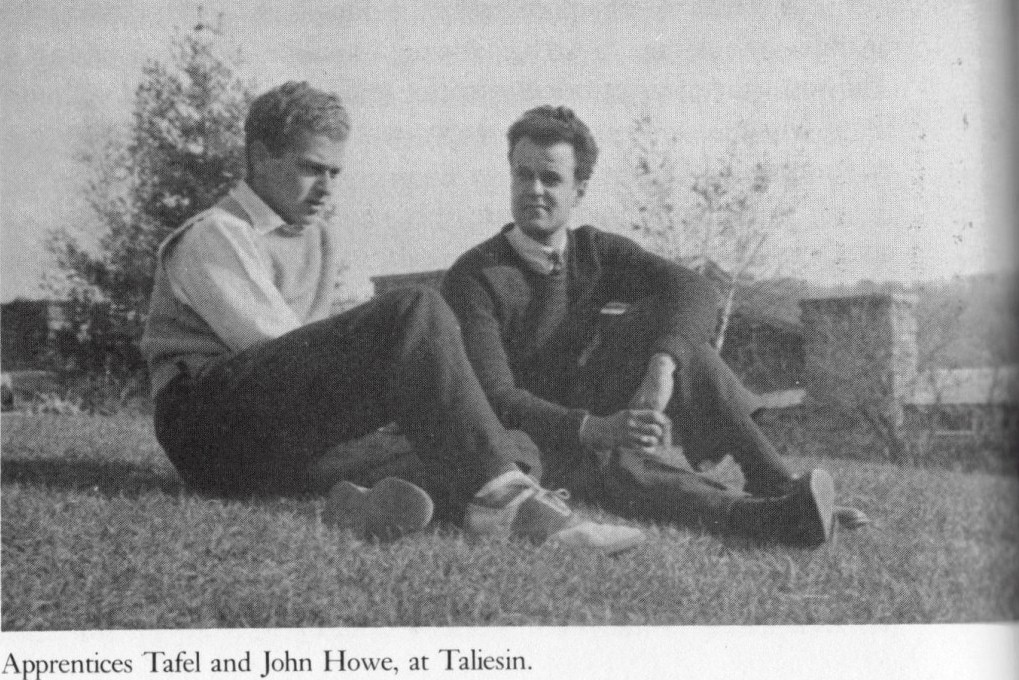
Taliesin Fellowship member, Edgar Tafel, wrote about this four-day excursion in Apprentice to Genius (I wrote about the book when I recommended it in March). Wright, Tafel wrote,
… had a great deal of respect for Mies’ work. He’d seen the Tugendhat house and the Barcelona pavilion in publications, and he viewed Mies as an individualist, not as part of a foreign school or movement.
Edgar Tafel. Years with Frank Lloyd Wright: Apprentice to Genius (1985; Dover Publications, Inc.; McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1979), 69.
Tafel went on to say that during the trip from Mies, Wright, “felt Mies’ warmth and was happy to have his work viewed with understanding.” [Apprentice to Genius, 71] Tafel also wrote that while,
Mies didn’t ask questions or make any comments, … he kept smiling and nodding his head in understanding. For a man of stolid, Germanic character, he was positively radiating.… We could see Mies sorting out each explanation and filing each experience away in the proper mental drawer.
Edgar Tafel. Years with Frank Lloyd Wright: Apprentice to Genius (1985; Dover Publications, Inc.; McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1979), 79.
Despite this spontaneous sojourn (with no toothpaste or clean clothes), Mies must have done ok. Aside from being an important guest (and probably getting to sleep in Taliesin’s “Big Guest Room” that tours walk through), he got to wander all over the Taliesin estate for days.
Be grateful it’s here
Bertrand Goldberg, however, had become the full-time translator with no way to leave. By the third day, Goldberg was complaining to Mies, in German, about Taliesin.
[Goldberg said later that he thought Wright’s home was “romantic kitsch”.]
Mies apparently got tired of listening to Goldberg’s complaints and finally said to him, “Shut up, Goldberg. Just be grateful it’s here.”
[Look at the table of contents in Bertrand’s oral history linked to above after Goldberg’s name to find where he discussed Taliesin]
Yet, while Mies appreciated Taliesin, Wright was unable to persuade the German architect to visit again.
This wasn’t for lack of trying
Mies took advantage of Taliesin’s proximity and, on five different occasions, asked Wright to entertain visitors.1 Every time Mies asked, Wright said yes, often including an invitation. But Mies never took him up on it. In 1944, Wright even invited Mies to celebrate Thanksgiving at Taliesin.2 Mies didn’t reply to that letter.
The most surprising exchange between the two came in 1947. That year there was an exhibition on Mies’ work at the Museum of Modern Art in New York City. Both men were at its opening and Wright, while there, (famously) said that the exhibit was “much ado about your next to nothing” (Mies was famous as saying, “Less is more”). Wright wrote to Mies3 soon afterwards, making sure that he hadn’t hurt Mies’ feelings with the remark.
I transcribed this letter on one of my trips to Wright’s archives. When I got to Wright’s words that
“I didn’t want to hurt your feelings,”
I had to stop and read them again. Because I wasn’t sure I was seeing it correctly. Biographer Finis Farr wrote that the “twinkle” in Wright’s eyes when he said things didn’t translate. But still, I never thought I’d see Wright actually say he didn’t want to hurt someone’s feelings.
Regardless, there was nothing for Wright to worry about. In his reply,4 Mies wrote that he hadn’t remembered Wright’s crack, but if he had, he would have laughed with him. Mies ended the letter by saying that he would enjoy coming back to Taliesin (where Wright had again invited him). However, as far as I know, Mies never returned.
First published May 17, 2021.
“… Love Him As I Do”: Wright said that was his introduction for Mies van der Rohe at a dinner at the Armour Institute. The story is in An Autobiography, by Frank Lloyd Wright, new and revised ed. (New York: Duell, Sloan, and Pearce, 1943), 429.
I took the two photographs at the top of this post: the photograph of the Edith Farnsworth house (the structure of glass and steel) on April 6, 2006; and the photograph of Taliesin (the yellow/beige structure surrounded by greenery with a blue sky) on June 6, 2005.
Notes:
1 The letters, with dates and the microfiche identification numbers:
From Mies to Wright arranging trips for friends or students to Taliesin:
10/12/1940 (ID #M108A01);
10/24/40 (ID #M108C09);
11/26/40 (ID #M110A09);
10/17/41 (ID #M120B04);
ID #M120D06 (I forgot the date, but it’s after Wright’s 10/22/1941 letter);
1/29/43 (ID #M127A09);
2/1/46 (ID #M152E03);
10/11/46 (ID #M155E03);
10/15/47 (ID #M167B07)
Wright’s replies to Mies’ requests:
10/14/1940 (ID #M108A04);
4/14/41 (ID #M116D07—this was a thank you letter from Wright in which he invited Mies to Taliesin, maybe that summer?);
10/22/41 (ID #M120B10);
10/13/46 (ID #M155E04).
2 Invitation for Thanksgiving at Taliesin, from Frank Lloyd Wright to Mies van der Rohe, 11/15/1944 (ID #M135E04)
3 Letter written 10/25/47 from Wright to Mies (ID #M167D09) in which Wright was making sure that Mies van der Rohe wasn’t hurt by his own statements at the opening of the Museum of Modern Art exhibit.
4 Reply written 11/25/1947 from Mies to Wright (ID #M168D08), telling Wright that he didn’t remember Wright making a “crack”, and that is would be pleasurable to see him “sometime in Wisconsin”.
This is an interesting page about Mies.