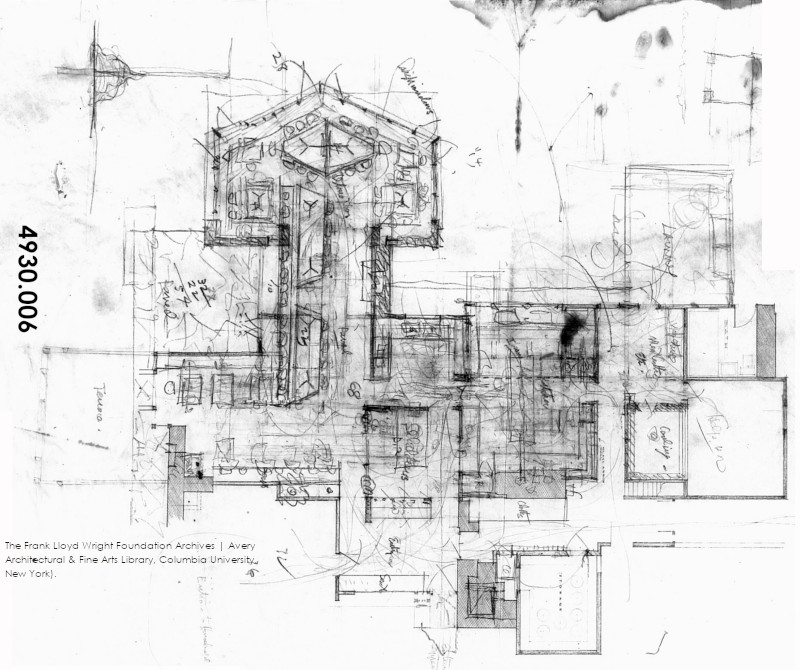
This is drawing number 4930.006 in the Frank Lloyd Wright Foundation Archives (The Museum of Modern Art | Avery Library, Columbia University, New York).
Two years ago I wrote here about when I found a Taliesin drawing of bunkbeds for a room at Taliesin in 1911.
srsly: someone needs to give me a commission for suggesting that the Frank Lloyd Wright Foundation use this to market Wright-designed bunkbeds.
My post today is about another Taliesin drawing I found.
Several months ago I went looking at the drawings that show Wright’s drawings related to buildings on the Taliesin estate.
I did that because researching things related to Taliesin makes me happy.
C’mon: you know you’re not surprised.
You can see the drawings from 1910 at the Wasmuth Portfolio and in a number of books. But you can see also a lot of online black and white photos in the Frank Lloyd Wright Foundation Archives here, through JSTOR.1
JSTOR is “part of ITHAKA, a not-for-profit organization helping the academic community use digital technologies to preserve the scholarly record and to advance research and teaching in sustainable ways.“
Every drawing in the Frank Lloyd Wright Foundation Archive has an identification number. The first four digits of each ID comprise the project number.
So, like, all drawings for Wright’s Guggenheim Museum commission start with “4305.”
The first two numbers are because the commission started in 1943. Bruce Pfeiffer (a member of the Taliesin Fellowship who became the archivist for Wright’s collection) numbered the Gugg as that year’s 5th commission. So: 4305.2
I’ve got the project numbers for all of Wright’s buildings on the Taliesin estate. So I searched for those numbers.
You can do it, too, if you have the time. Just go to this page. Might not be something you want to do in the summer, but you could. Sure, you could!
One of the building projects that I studied was labelled:
#4930
4930 were drawings executed during the planned renovation of the “Home Building” at Hillside. Hillside is one of the buildings on the Taliesin estate. If you’ve taken a tour that went anywhere near the Hillside building, your guide might have told you about the Home Building. It stood there from 1887-1950, and is part of the site’s history.
In 1887, Wright designed the building for his aunts, Jennie and Nell Lloyd Jones when they were planning their new school (see the whole history of it here).
You can find lots of photos of the Home Building at the Wisconsin Historical Society. Here’s one below:
From a postcard. Photo taken 1887-1915 (although probably pre-1915). Looking northwest at the Home Building. The postcard says “Hillside Home School”, which was the name of the school, but not the name of the building. Wright’s later Hillside Home School building (the stone building) was built to the left of the building you see in the photo.
When Wright published his autobiography in 1932, he described the building as
[D]esigned by amateur me and built by Aunt Nell and Aunt Jennie in 1887 to mother their forty or fifty boys and girls.3
Actually, he was so young when he first designed it, that none of the detailed drawings survive.4 But here’s part of what Aunt Nell wrote to the young Wright after he’d arrived in Chicago:
…. Do not take time to make elegant drawings if you are busy but send a rough sketch of what you think the best plan as soon as you can – as we hope to get men at work upon it as soon as the ground is fit in the spring….
I write in great haste but with much love –
Aunt Nell 5
Really: it was not a bad building for a 19-year-old to design.
After Wright’s aunts closed their school in 1915, the building and grounds stood idle for years.
Then,
in 1932 he and wife Olgivanna started the Taliesin Fellowship (his apprentice program).
The photo below
Shows work taking place at the Home Building. Apprentice Edgar Tafel took it and it’s published in his book, Apprentice to Genius. The photo was taken in 1932-33:

Looking northeast at two people working near the Home Building during its initial renovation. Photo in Apprentice to Genius, p. 29.
We saw this side of the building in the earlier photo. In the photo above, we’re looking northeast. In the earlier photo, we were looking northwest.
Apparently, he wanted to do a lot more, but he never got around to it.
Yet in 1949, he addressed the building again.
And that’s how come,
Bruce numbered this collection of drawings “4930”.
When I looked at them, I realized one of them wasn’t the Home Building at all.
It’s drawing 4930.006 and
it shows the old dining room. At Taliesin.
Check it out:
I put a drawing of the old dining room on the left and the drawing in the 4930 collection on the right:
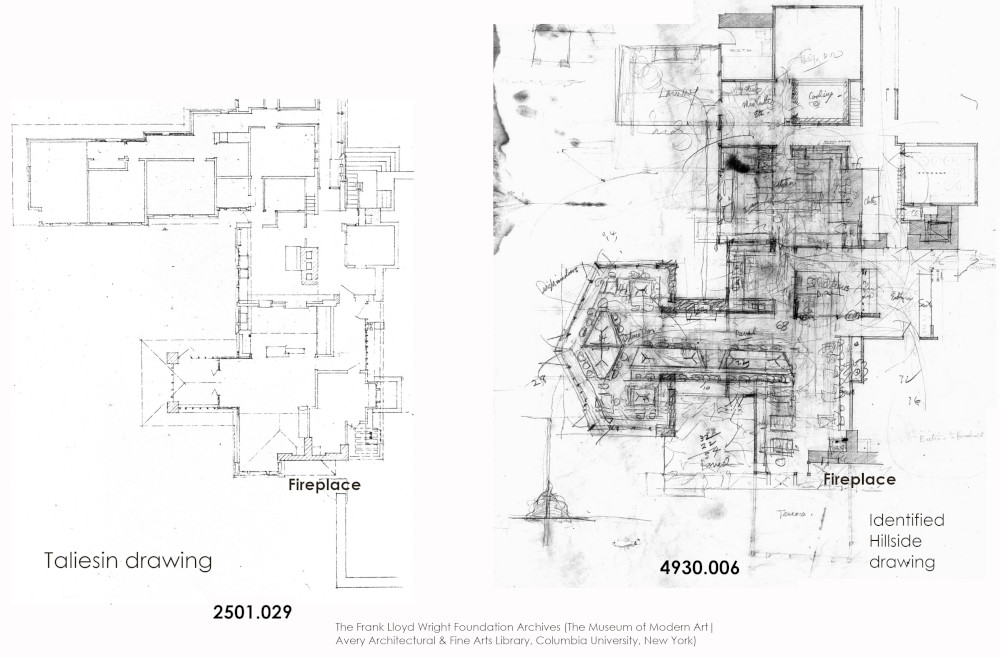
The first thing you can see is the fireplace.
It’s shaped like an upside down “T”.
Not that far from it is the “entry” and the “cooling” room, just like they were in that part of the building. You can see where Wright drew little tables and chairs in figuring out the seating.
After looking, I sent the compared drawings to Kyle Dockery, the Wisconsin onsite Collections Coordinator for the Frank Lloyd Wright Foundation.
He agreed that I found another Taliesin drawing and that 4930.006 shows Wright’s thinking about expanding the room. Which is why he had that large part (also shaped like a “T”) coming off on the left.
After this, I wrote my thoughts to someone at the Avery Library, since they have the drawings. I gave them my theory and sent them the comparison drawings. Shelley (from the Avery) wrote me back, agreeing with me and thanking me for my “meticulous eye”.6
By the way:
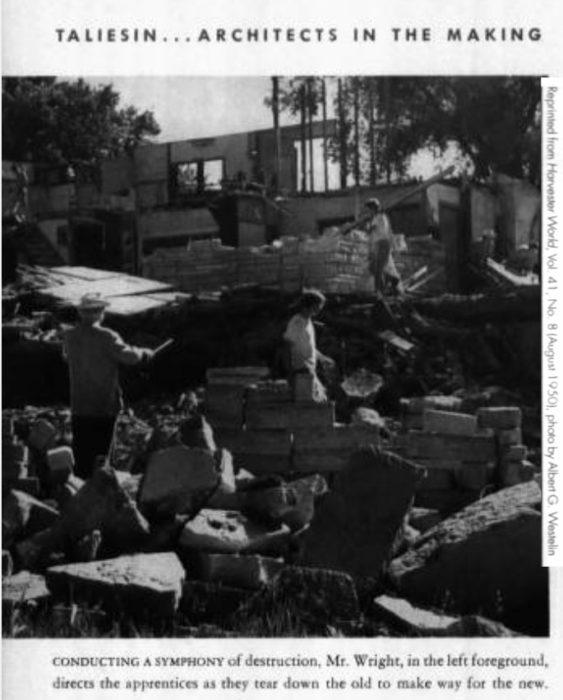
Wright halted the renovation of the Home Building in 1950 and ordered his apprentices to destroy the building.
That lead to this fantastic photo of Wright conducting, as the photo’s caption says, “a symphony of destruction”:
You can see it on page 6 of The Harvester World at the Wisconsin Historical Society. The image above links to that page of the magazine.
Why did Wright get rid of the Home Building?
It was part of Wright’s “cleaning up” of Hillside over the years. I think he did this because Hillside became his testing ground for large-scale designs. Here’s a photo of the walk up to Hillside that he created:
 Photograph that Maynard Parker took for House Beautiful magazine in 1955. Looking east at the Hillside Home School structure.
Photograph that Maynard Parker took for House Beautiful magazine in 1955. Looking east at the Hillside Home School structure.
Previous to 1950, you really could not have gotten a view like Parker’s in the photo above. That’s because Home Building would have stood right in the way of the photographer.
First published July 2, 2023.
The drawing at the top of this page is property of the Frank Lloyd Wright Foundation and is from The Frank Lloyd Wright Foundation Archives (The Museum of Modern Art|Avery Architectural & Fine Arts Library, Columbia, New York).
Notes:
1. Prior to late November 2024, the link took you to ARTSTOR, “a nonprofit organization that builds and distributes the Digital Library….” That changed in August to JSTOR.
2. I think the second number is the commission for that year. No one ever told me, but it seems logical.
3. Frank Lloyd Wright. An Autobiography (Longmans, Green and Company, London, New York, Toronto, 1932), 129.
4. One was published at the time in Inland Architect. It’s on this page.
5. Nell Lloyd Jones to Frank Lloyd Wright on March 9, 1887. FICHEID #: J001A03
6. Someday I’d like to get to the archives and look at everything they haven’t identified.