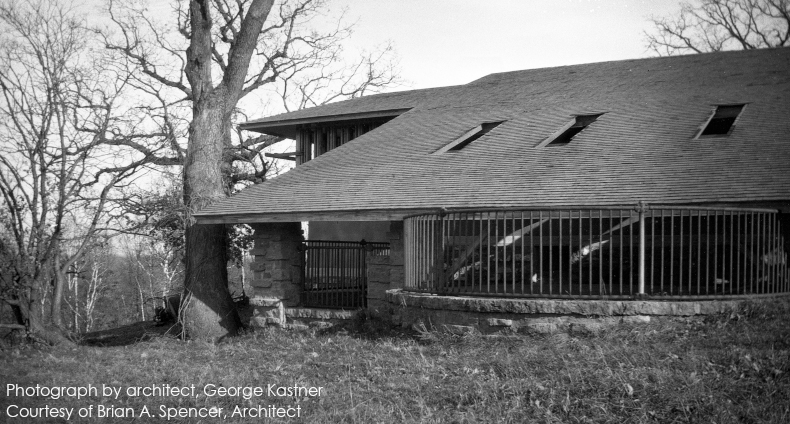
George Kastner took this photograph on November 28, 1928. It’s looking northeast at the far western end of Taliesin.
“I don’t know why you say it was a pigsty,” Minerva said to me (Minerva became a member of the Taliesin Fellowship in the 1950s). “It always had goats.”
She was referring to a section at the end of Taliesin. It’s rectangular, with a shed roof, and stands over a sandy area. It’s never been lived in. I’d heard it was called a pigsty because Frank Lloyd Wright had the label “Hog Pens” in it, the first time it appeared in a drawing. You’ve seen part of this drawing before, but this part (below) shows the far western part of the Taliesin structure. “Hog Pens” is there, in and outline:
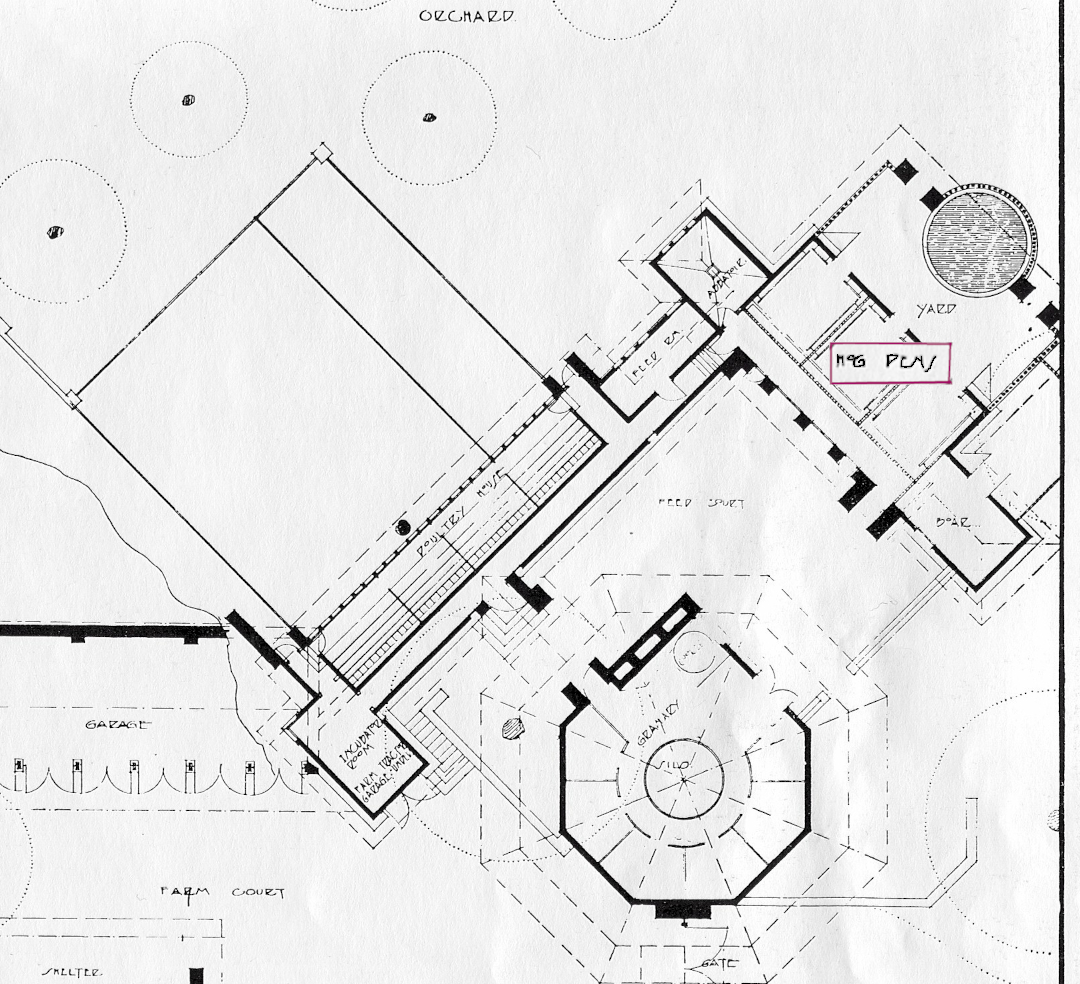
The drawing was originally published in Wendingen Magazine during issues it published on Wright in 1924 and 1925.
Then the magazine issues were published as a book, The Life-Work of the American Architect Frank Lloyd Wright, by Frank Lloyd Wright, H. Th. Wijdeveld, ed. (Santpoort, Holland: C. A. Mees, 1925).
Most of what you see in the drawing was designed as the “Farm Court”. It had the hog pens, a yard with a circular pool for the pigs, and a room on the right placed there for the boar.
Moreover,
90 degrees to the left of the Hog Pens was the poultry house. This space contained the entire chicken life cycle:
- the “incubator room” (for hatching eggs),
- the chicken coop (raising the chickens),
- and the abattoir (slaughtering them).
Between the poultry house and the pigsty/goat pen was the octagonal “Granary” with circular “Silo”.
Those two were never built. Even though Wright had drawings showing them.
See — I told you not to trust the drawings. But you didn’t listen to me, did you.
All of these spaces (for hogs, chickens, and feed) are related to the photograph that is at the top of today’s post. And that’s what I’m going to write about today.
Architect, Brian A. Spencer gave me the copy of the photograph at the top of this post. This, and other photographs of Taliesin were taken in 1928 by George Kastner.
Kastner appeared in my post “Oh My Frank: I Was Wrong” and one of his photographs is in “Wall at Taliesin’s Garden Court“.
Kastner arrived at Taliesin to work under Wright on November 20, 1928.1 His dated photographs give us a certain date on details at Taliesin. Better yet, Kastner labelled the photographs on the back!
What did he write on the back of the photo at the top of this post?
Unfinished Wing
So, even though this part of the building had been around since 1924 (according to that drawing and photos 2 ) it was, according to Kastner (or Wright), “unfinished”.
Did Wright ever use this part of the building the way he originally planned?
Well, we know this was built after 1920.
How do we (ok: mostly me) know that?
The Pigsty/Goat pen was added after the November 1920 drawing by Rudolph Schindler (I referenced the drawing in a post in late 2021).
And this part of the building existed by 1924 when the Tsuchiuras (Kameki and Nobuko) were at Taliesin.
But, then what? Did he ever have pigs there?
So, here’s what I did to find that out:
I investigated whether or not Wright had the time to finish this part of the building, what with a fire and bankruptcy and all that crap.
Although, I didn’t really do this. I just knew the work of the ones that did. 3
So, Wright’s life in the 1920s is abbreviated below:
1922
In August, Wright comes back from Japan after working on the Imperial Hotel for years. But, he probably didn’t have time to construct the farm wing before the winter set in. And he might have held off while trying to settle into other commissions. Because, in
1923
he’s in Los Angeles working on commissions from February through late September.
Then he was back at Taliesin in October and November, when he married his second wife, Miriam Noel. Then he was in California again from December until
1924
the end of February.
He’s back in Wisconsin near the time of the death of his mentor, Louis Sullivan (Sullivan died in Chicago on April 24).
Miriam Noel left Wright by late April/early May.
Wright stayed put at Taliesin for most of the rest of the year.
He meets Olgivanna in late November after a trip to Chicago to see the ballet with a friend.
Looking at the dates and Wright’s availability, I think that 1924 was when Wright built what’s in that drawing: a chicken coop, hog pens, incubator room, and sure, parking spaces. He had the time, and perhaps thought it was time to get some farming done in Wisconsin (Wisconsin is the Dairy State after all).4
1925
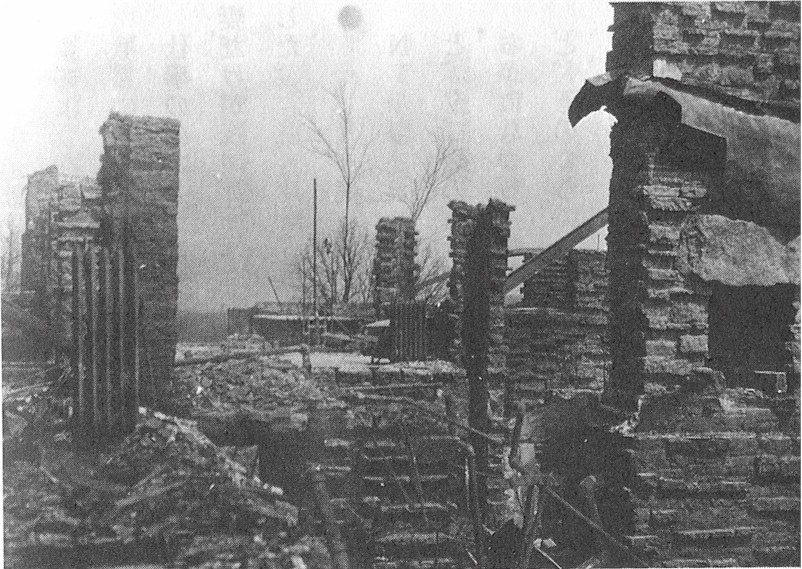
In the beginning of this year, Wright, along with his new love Olgivanna and her daughter, Svetlana, was living at Taliesin. In April 20 of that year, the second Taliesin fire happens.
That fire certainly pulled him away from thinking about the chicken coops on the other end of the building. So, Wright redesigned and rebuilt Taliesin’s living quarters for most of the remainder of 1925.
Then
In early December, Olgivanna gave birth to her and Wright’s daughter, Iovanna. The life of Wright and the three other people in his life (Olgivanna and the two daughters) for lots of reasons having
NOTHING TO DO WITH FIRES
goes off the rails for years. Due to this, Wright sure didn’t have a lot of time to think about being a dandy country farmer.
And, while that part of the building did eventually have chickens (for years), George Kastner’s 1928 photograph says that the entire western side of the building was not, for years, used for farm work.
Originally published July 25, 2022.
The photograph at the top of this post is the property of Brian A. Spencer, architect. Used with permission.
Notes:
1 Kastner and others lived with the Wrights at the camp Wright designed in Arizona, Ocotillo. Several of Kastner’s photographs are in the article, “Desert Camp Memoir: George Kastner and Frank Lloyd Wright”, in Journal of Organic Architecture + Design, vol. 7, no. 3, 2019.
2 I can’t show you the photos of that part of the building in 1924. They’re not owned by me and I have never been in contact with the person or institution that has the rights to them. The owners would be really (and justifiably) pissed off if I showed them. But I was able to show the photo of Taliesin after the 1925 fire photo months ago, because it’s published in a book. Although if anyone wants to get in touch with the owners and give me a call I’m sure I could do a good job writing about them.
3 Wright scholars have figured out Frank Lloyd Wright’s activities 1911-32. I found this information by looking in the books, FLLW: Designs for an American Landscape (185-201) (link to the Library of Congress exhibit web page, here); Meryle Secrest’s biography, FLLW: A Life, the book, FLLW: 1910-22, The Lost Years, by Anthony Alofsin, and “Wright and the Imperial Hotel: A Postscript,” by Kathryn Smith, Art Bulletin 67, no. 2 (June 1985).
4 ALTHOUGH, in some sort of Wisconsin crime against all that is perfect, the website “www.comesmellourdairyair.com” is owned by someone from outside of the state. Why, Vicarious Ranch in California of all things! They’ve got goats, pigs, lambs and a creamery, which sounds wonderful, so I hope they make a good living.



