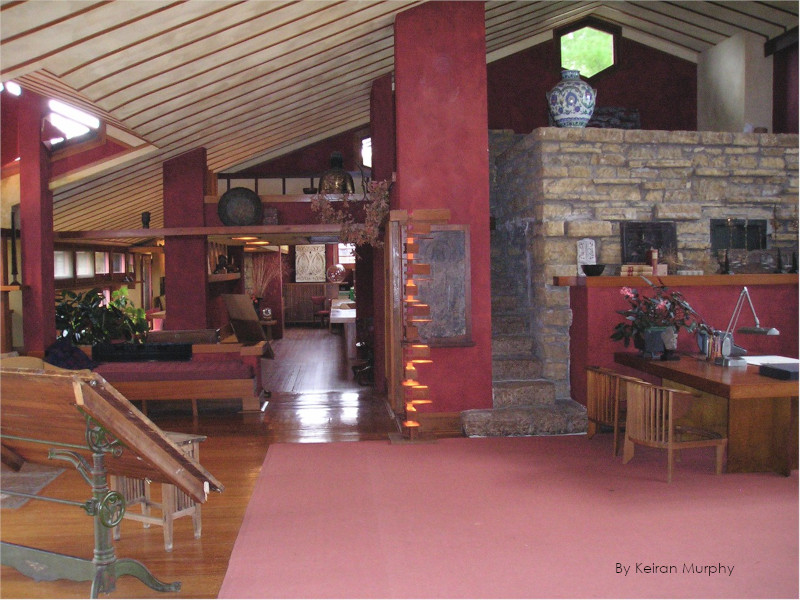
We hear he liked music,
if you didn’t know that, just trust me
but what is this thing about a Musical Note?
I’m talking about a retaining wall outside of Taliesin and I’m going to write about it today.
It’s called that because
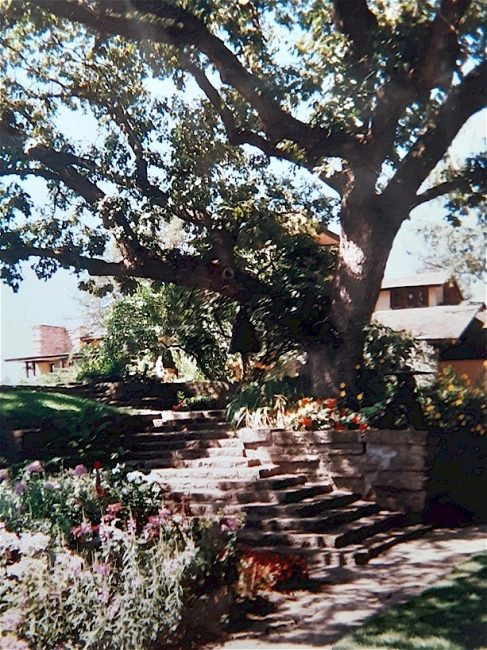
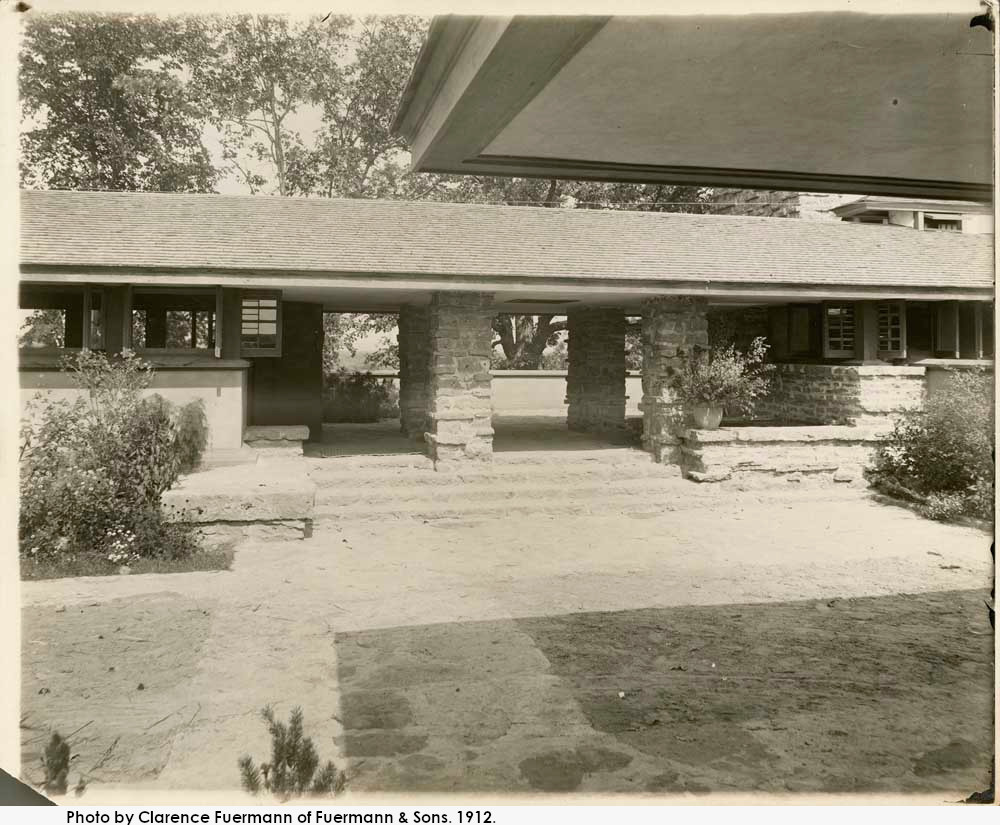
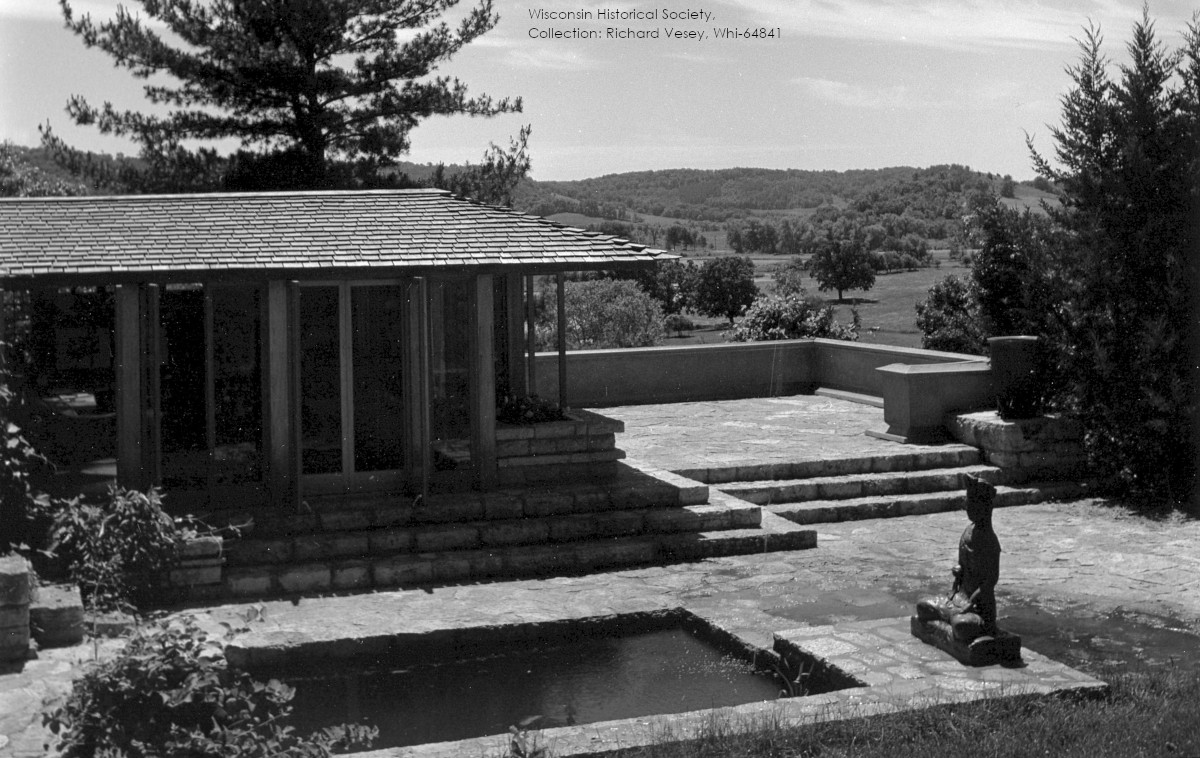
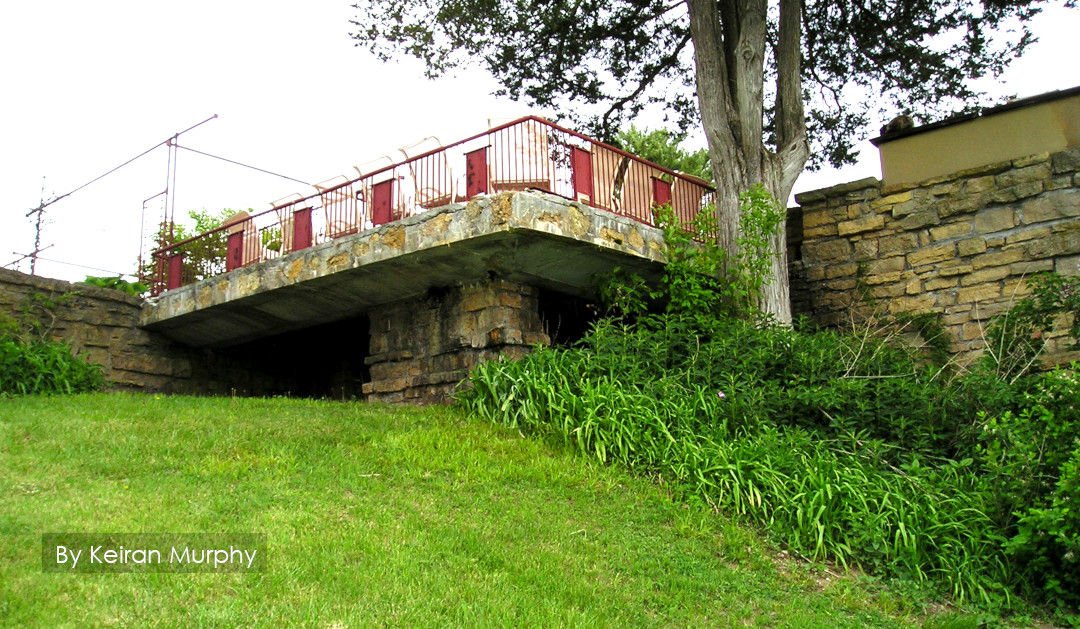
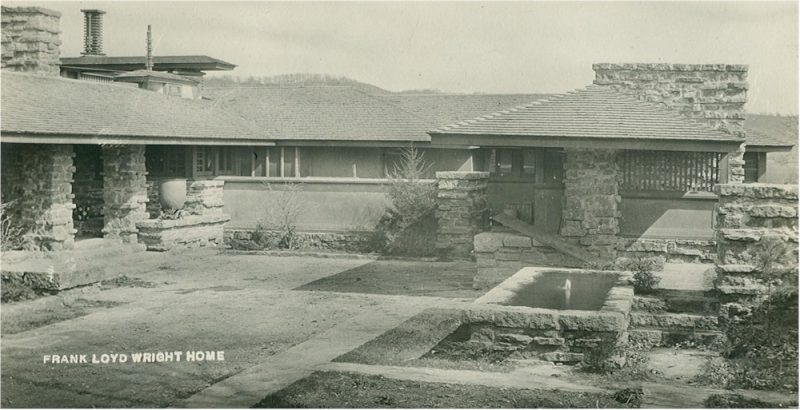
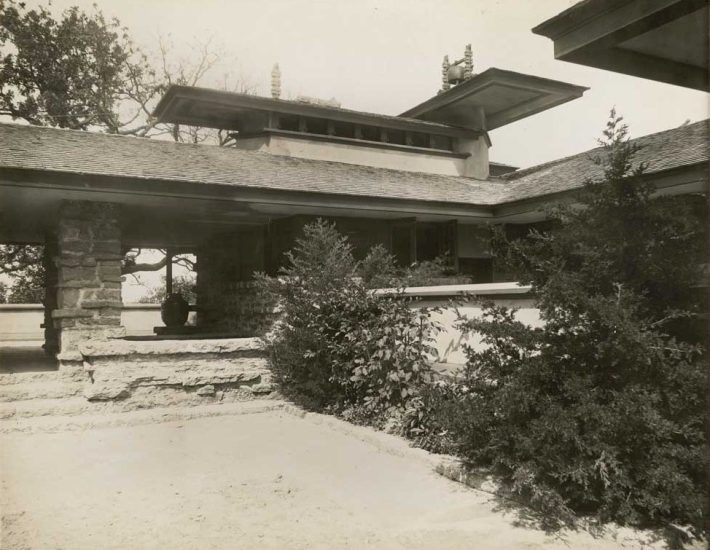
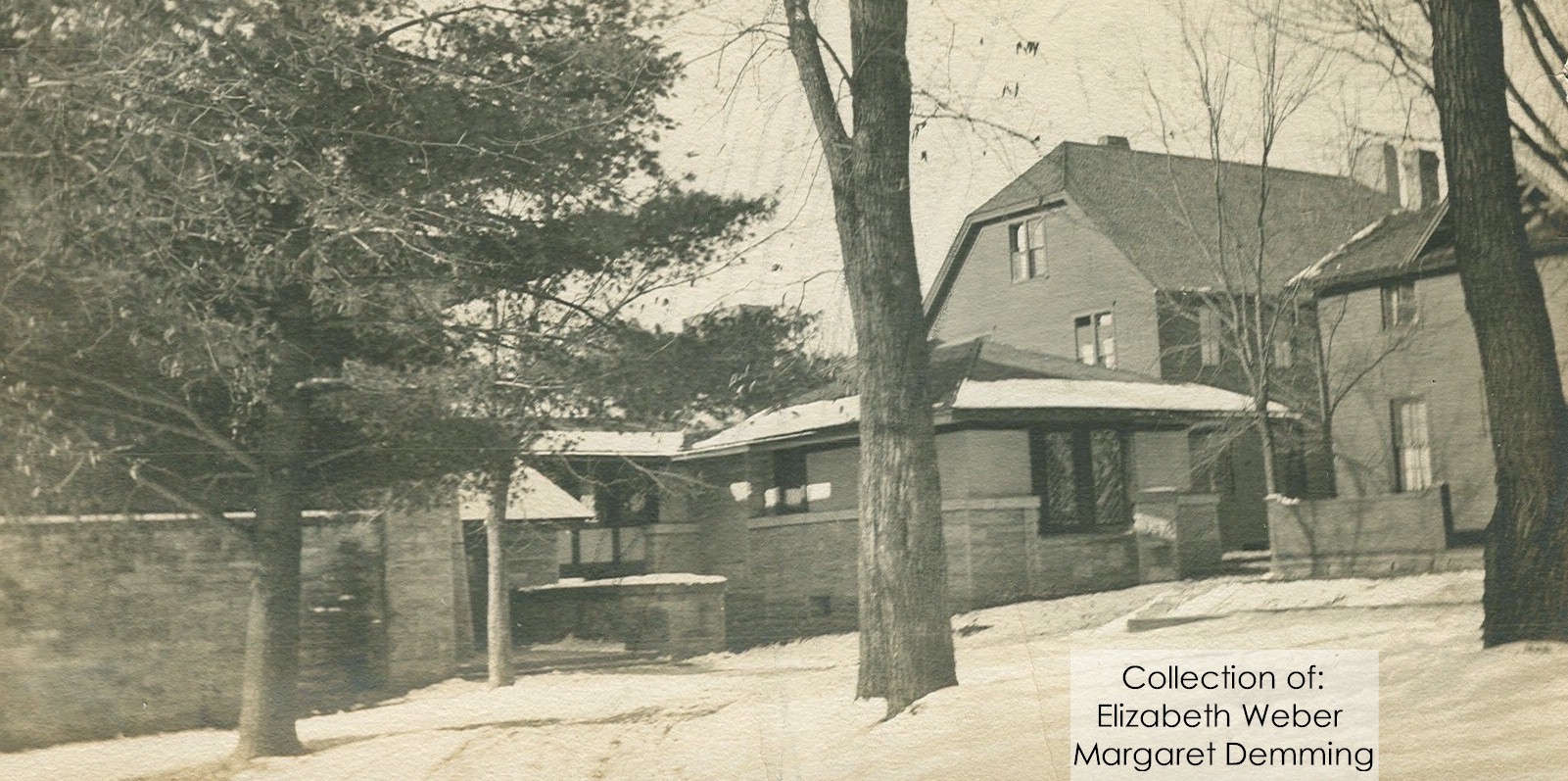
It looks like two musical quarter notes touching end-to-end.1 You can see it in the historic photo at the top of this post, just left of center.
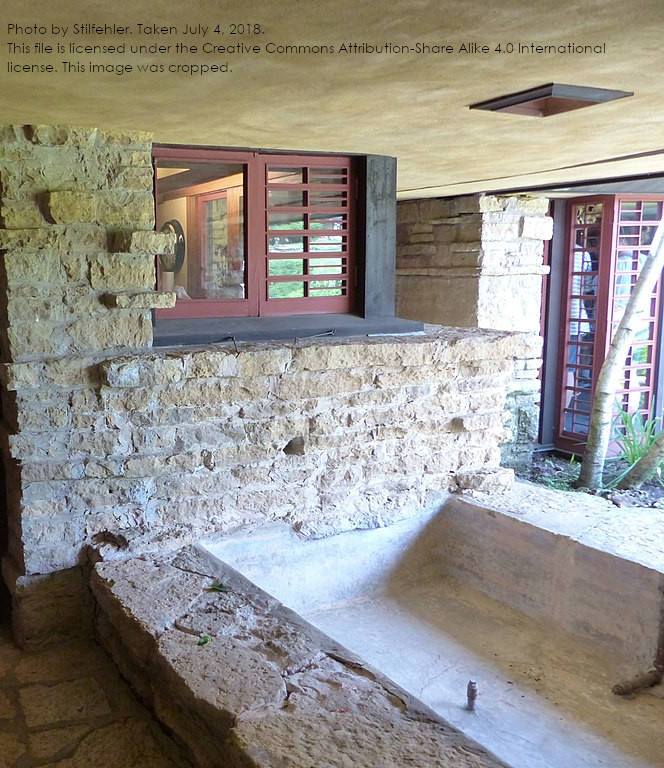
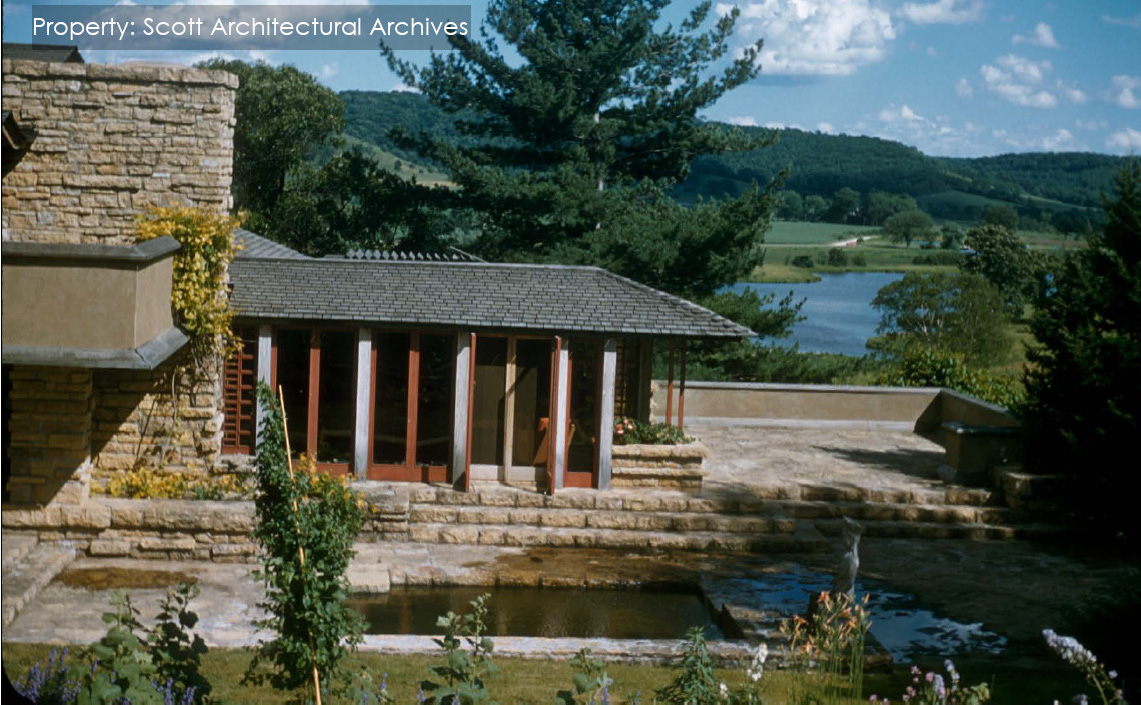
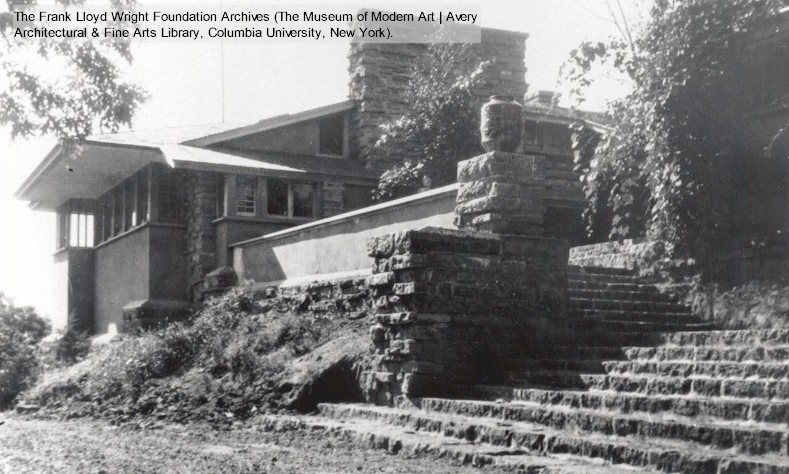
And you can see it in the modern-day photo below:

Used with permission.
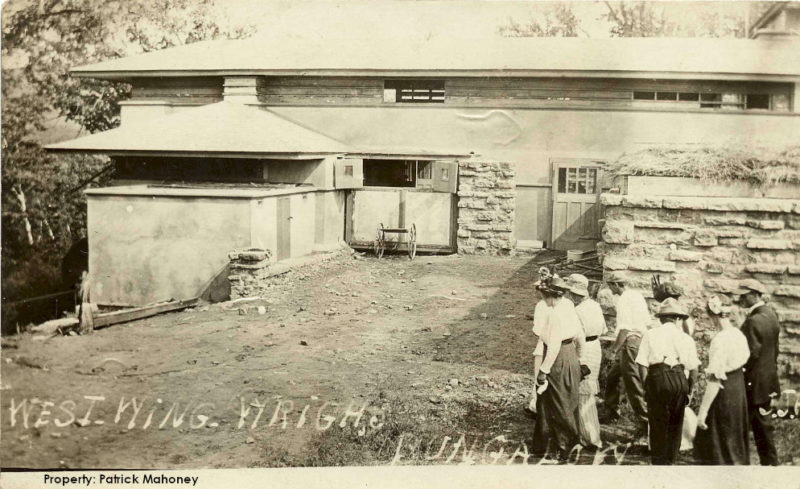
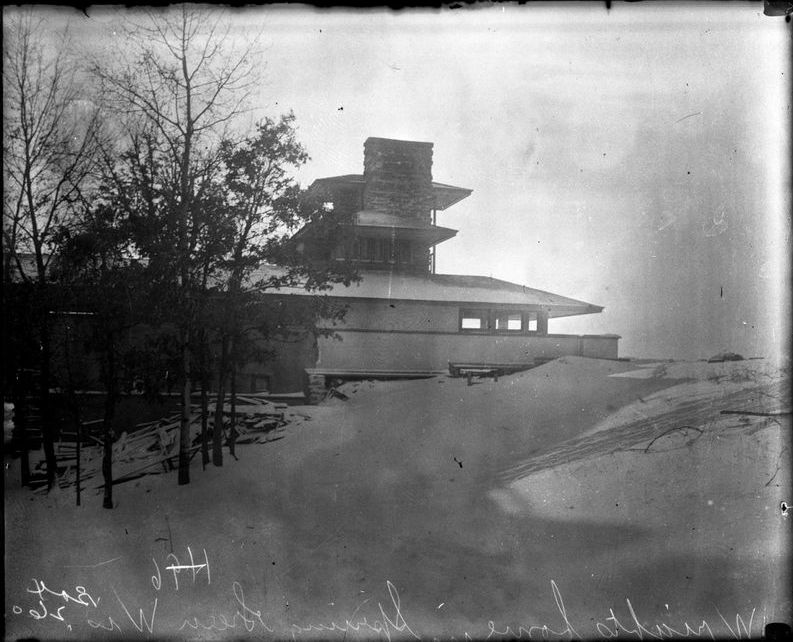
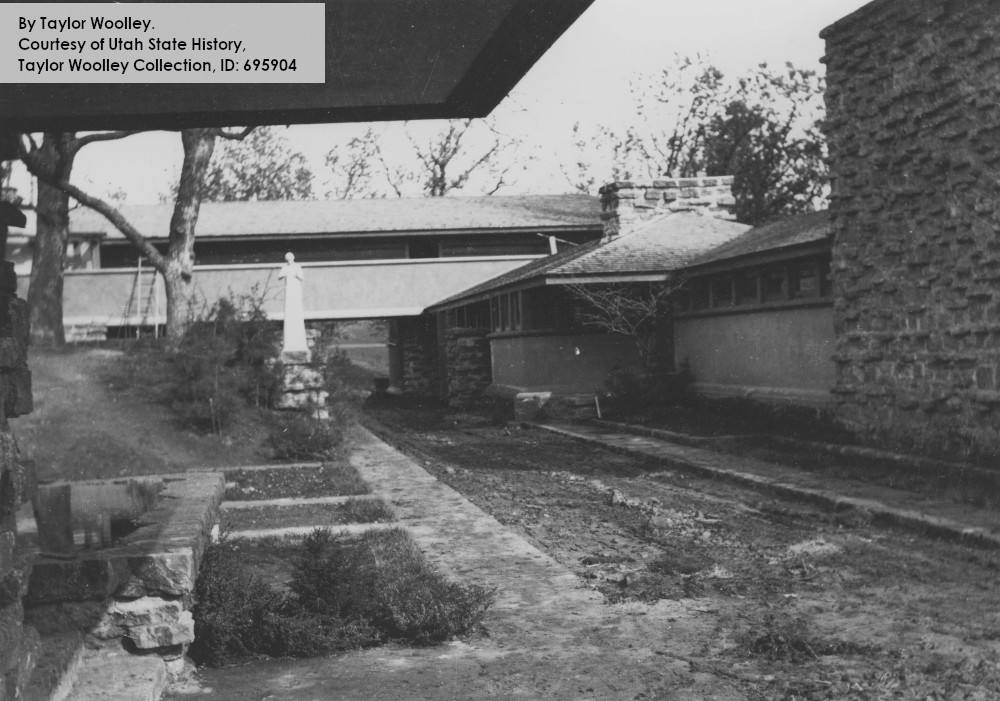
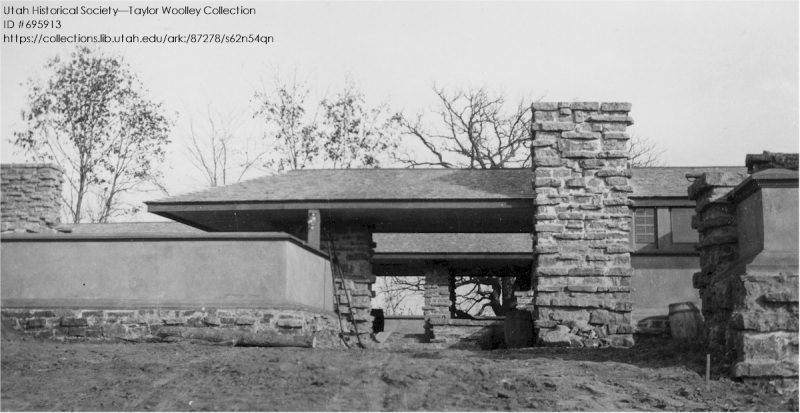
The wall seems to have shown up after 1912, based on other photographs at the Wisconsin Historical Society. For instance, this really old photo of Taliesin doesn’t show this wall at all:
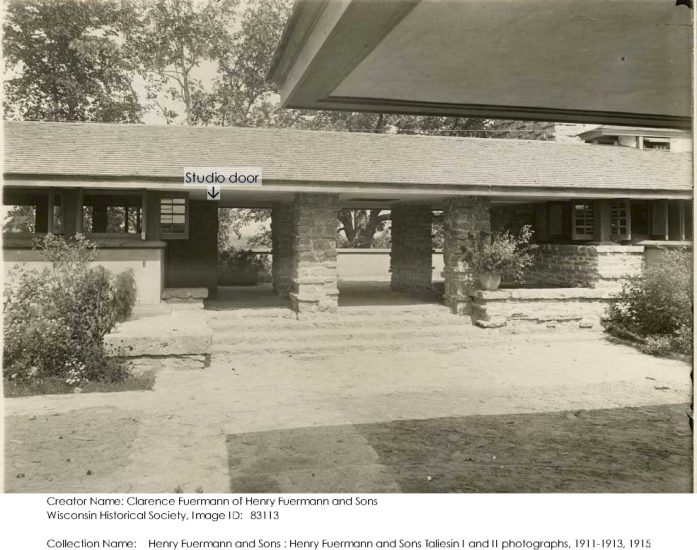
 Looking northwest (plan direction) at Taliesin’s living quarters, 1911-12. Given the configuration of the building, it looks like this was taken during Taliesin’s first winter.
Looking northwest (plan direction) at Taliesin’s living quarters, 1911-12. Given the configuration of the building, it looks like this was taken during Taliesin’s first winter.
Then there’s one taken in 1912 by Clarence Fuermann of Henry Fuermann and Sons; and if you look closely at it, something has been built in the area, but not the retaining wall.
But we know he was doing something around there in 1913.
We know that because on June 19 of that year, The Weekly Home News2 stated that:
Work has started at Frank Lloyd Wright’s summer home. B.F. Davies3 has a crew of men laying water mains, which will supply all the buildings with water and also irrigate the gardens, vineyards and flower beds.
All of these things help to get water to the gardens, which Wright wrote in his autobiography that each court at Taliesin:
… had its fountain and the winding stream below had a great dam. A thick stone wall was thrown across it, to make a pond at the very foot of the hill, and raise the water in the Valley to within sight from Taliesin. The water below the falls thus made, was sent, by hydraulic ram, up to a big stone reservoir built into the higher hill, just behind and above the hilltop garden, to come down again into the fountains and go on down to the vegetable gardens on the slopes below the house.
An Autobiography, by Frank Lloyd Wright. In Frank Lloyd Wright Collected Writings: 1930-32, volume 2. Edited by Bruce Brooks Pfeiffer, introduction by Kenneth Frampton (Rizzoli International Publications, Inc., New York City, 1992), 226.
This is the second time I posted this quote. The first time was about whether or not Taliesin had outhouses. You don’t know?! Well check it out.
Of course I’ve thought about that. I think I’ve mentioned on here that sometimes I walk through Taliesin in the past to relax myself before sleeping.
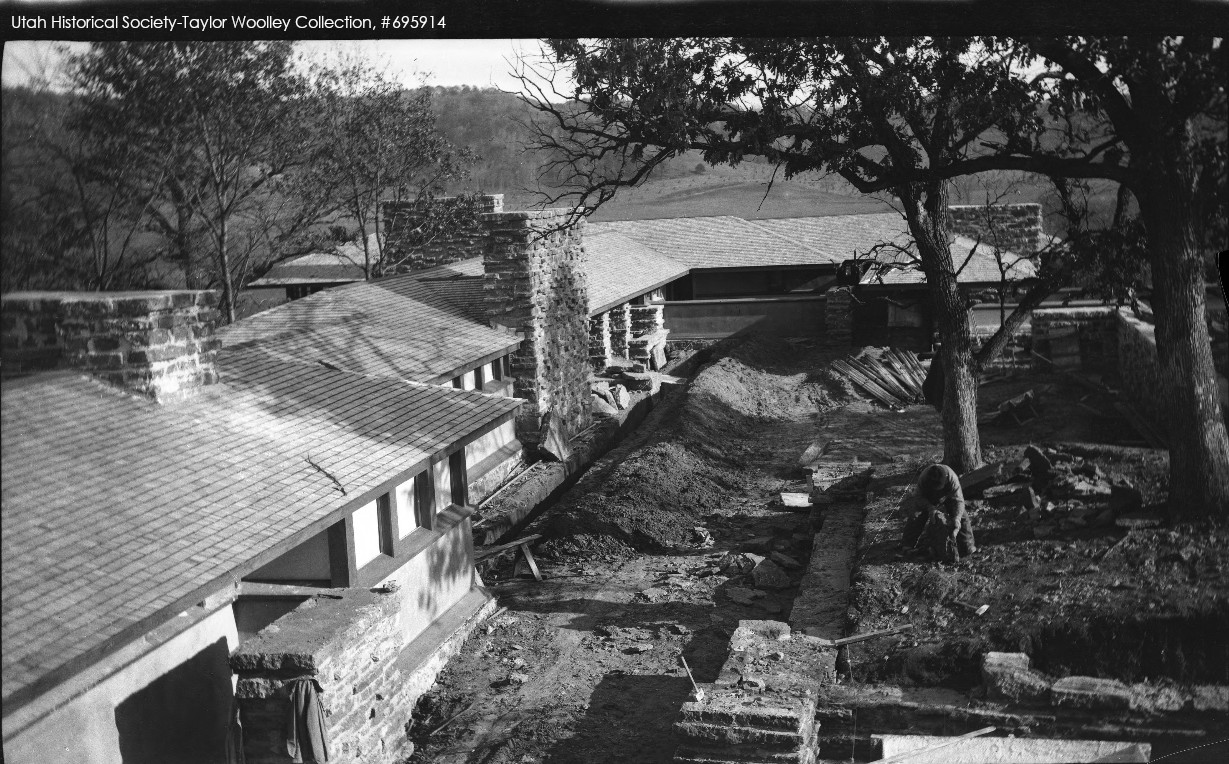
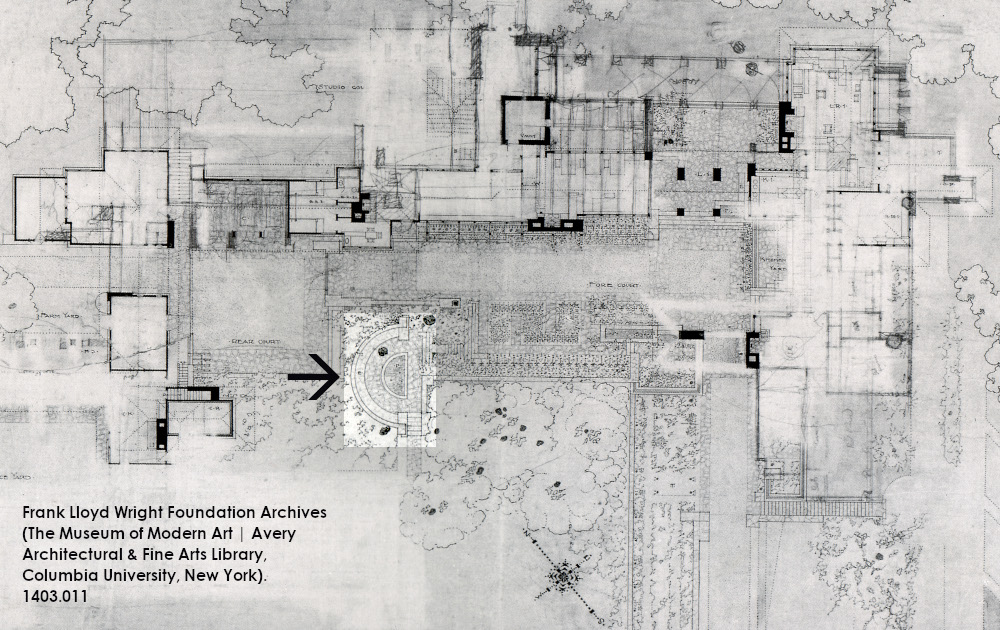
Still, we can only confirm that Wright built the “notes” (the circular parts at either end of the wall) during the Taliesin II era. One of those Taliesin II images is at the top of this post.
And,
those “notes” maybe may have been functioning cisterns.
After all, that part of the hill faces mostly south, which means that it gets a consistent amount of sunlight, so it’s a place Wright, in the earliest years was trying to get vegetables grown while trying to make a go of it out here in the country.
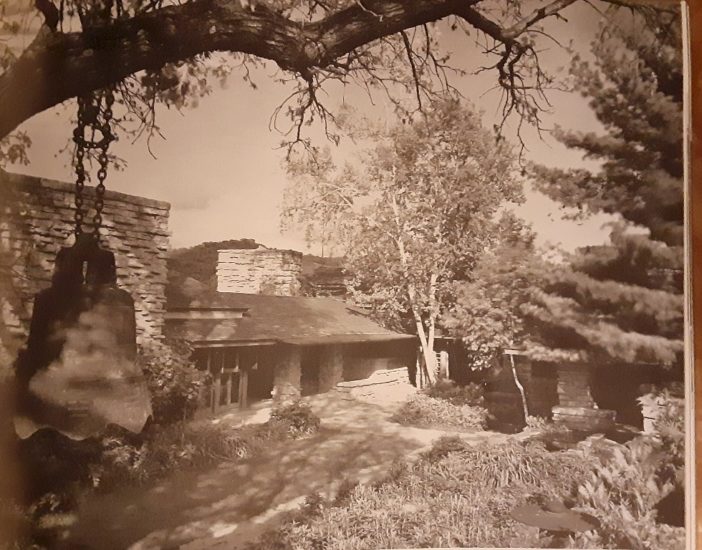
A good Taliesin II photo of planting grids on the southern part of the hill, is below. I’ve pointed out one of the “notes” on the retaining wall:

Looking (plan) northwest at Taliesin’s Living Quarters, 1915-21. This photo is printed in the book, Frank Lloyd Wright Collected Writings, volume 2, p. 145.
But I have no idea what he could have been growing in those grids.
btw: anyone who knows me knows I have a black thumb.
Anyway,
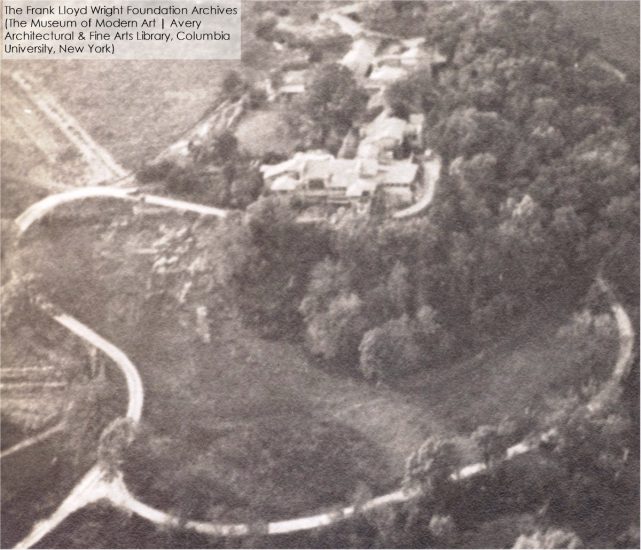
So, if they were cisterns, Wright stopped using them. Probably, once he expanded his land holdings, he could grow vegetables in all the other spaces as he bought more surrounding land. Yet, while he eventually had no reason to use the stone structure, he still kept it. Like what you can see in the Taliesin 3 aerial photo, below:
 Photo published in Frank Lloyd Wright: Complete Works, volume 2, 1917-1942, by Pfeiffer, Bruce Brooks (Taschen, 2009), p. 145.
Photo published in Frank Lloyd Wright: Complete Works, volume 2, 1917-1942, by Pfeiffer, Bruce Brooks (Taschen, 2009), p. 145.
When I first started giving tours, we walked up to the house and took a rest at that retaining wall to catch our breaths. While they sat on the wall, I’d invite my guests to look at the view while I started telling Taliesin’s story.
nowadays, folks on the Taliesin Estate tour still walk past there before going up to have their break.
In fact,
I remember plenty of days in my earliest years in which I repeated the myth about Taliesin’s 1914 fire that the murderer “sealed all of the entrances to the House“.
Information about this retaining wall probably isn’t common knowledge at Taliesin. But a lot of people can see it on tours, so there’s a bit of info for you.
First published on October 1, 2024.
The photograph at the top of this page was taken by Clarence Fuermann of Henry Fuermann and Sons. I talked about the Fuermann photos in my post about the Flower in the Crannied Wall statue.
Notes:
1. p.s.: I don’t think Wright ever referred to it that way, but that’s what we all call/ed it in Taliesin tours.
2. Spring Green’s newspaper.
3. I think I might have found B.F. Davies in the census. Wright wrote to a “Ben Davies” several times in the late 1920s.